
Last updated: February 2023
There's a fair amount of confusing terminology to wade through when considering an electric heating system - especially if you're new to electric heating. Do you need electric heaters or convection heaters? Electric radiators or electric heaters? Are panel heaters the same as electrc radiators? To provide answers, let's explore the differences and similarities between both products.
Electric radiators
Honestly, “radiator” is one of the most ambiguous and misused words in the heating industry. Technically, the word “radiator” should only refer to heaters that heat primarily through radiation - the same way an open fire warms your hands. In reality, however, the word “radiator” is widely used for a range of products – even gas central heating radiators, which often heat primarily through convection. Our energy efficient electric radiators use a combination of radiated and convected heat for effective comfort heating.
Electric heaters
Electric heaters, also known as panel heaters, is the name sometimes given to budget convection heaters sold at the bottom end of the electric heating spectrum. You may confuse them with products such as infrared panel heaters, understandably due to the words ‘panel’ and ‘heater’ being used in both cases. But infrared panel heaters are top-of-the-range electric heating products, which heat solely via radiation. The main difference between panel heaters and our electric radiators is that the panels mainly produce heat through convection, typically using hot elements to push out hot air that later circulates around the room. Heating purely by convection comes with some disadvantages, but today we'll focus on the differences.
What's the difference?
So, why do electric heaters and panel heaters, seemingly designed for the same purpose, differ so much in price from electric radiators?
For example, the iQ Plus and the RC Wave: they feature similar technology, they look alike, and, after all, they are both technically electric heaters, but there are some key differences to consider. The table below briefly outlines these differences, providing a quick and easy comparison to help you determine whether electric heaters or electric radiators would be best for your space.
| Electric Heaters | Electric Radiators |
|
For occasional heating e.g. spare bedroom or conservatory |
For primary heating e.g. kitchen, living room or bedroom |
|
Heats through convection – solely warms the air |
Heats through radiation and convection – warms air as well as surrounding objects |
|
Less efficient – heat lost easily to draughts, so more power is needed to keep the space consistently warm |
Better efficiency – heats on a deeper level and warmth isn’t lost as easily so less power is needed |
|
Often more lightweight for better portability |
Less likely to disturb the air and agitate allergies |
|
Initial cost tends to be cheaper |
Which is best for me?
This table demonstrates that efficiency is one of the main factors that separates electric heaters and electric radiators. Where electric radiators, like the iQ Ceramic, are designed for everyday primary heating, electric panel heaters should be treated as an addition to your main heating system. They are a great way of providing supplementary warmth on top of your primary heating, whether that's electric or gas. Electric panel heaters are nowhere near as efficient when used to heat a whole house. They can be great conservatory heaters, garage heaters or guest bedroom heaters, but your own bedroom or dining room will likely benefit more from an electric radiator. This is simply down to the science of the way they provide you with warmth. Heating by convection is inherently less efficient than heating by radiation.
Convection vs Radiation
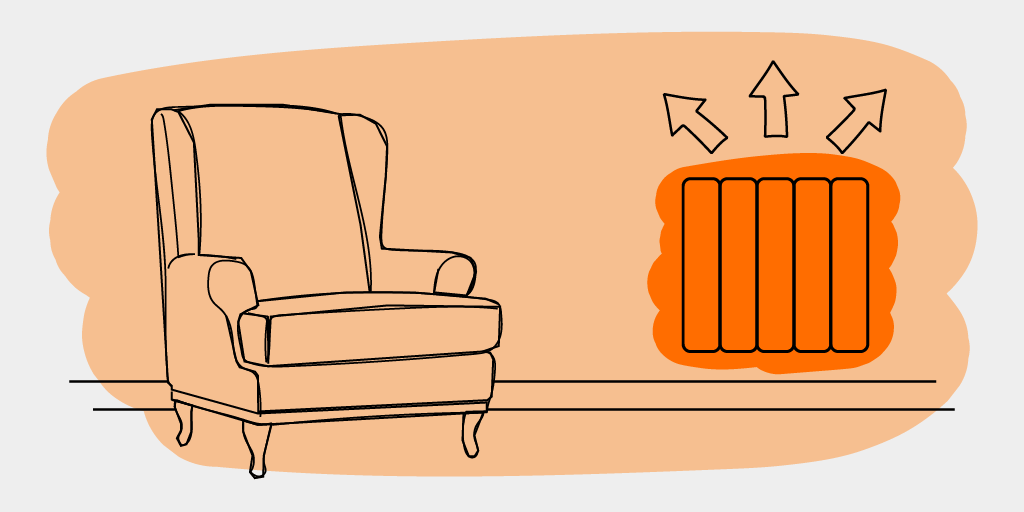

Convection transfers heat by warming the air. Heat is transferred first from the heater to the air, and then from the air to the objects in the room – which is much less efficient. This means that you will need much more power to effectively heat a room with a convection heater than you would with an energy efficient electric radiator.
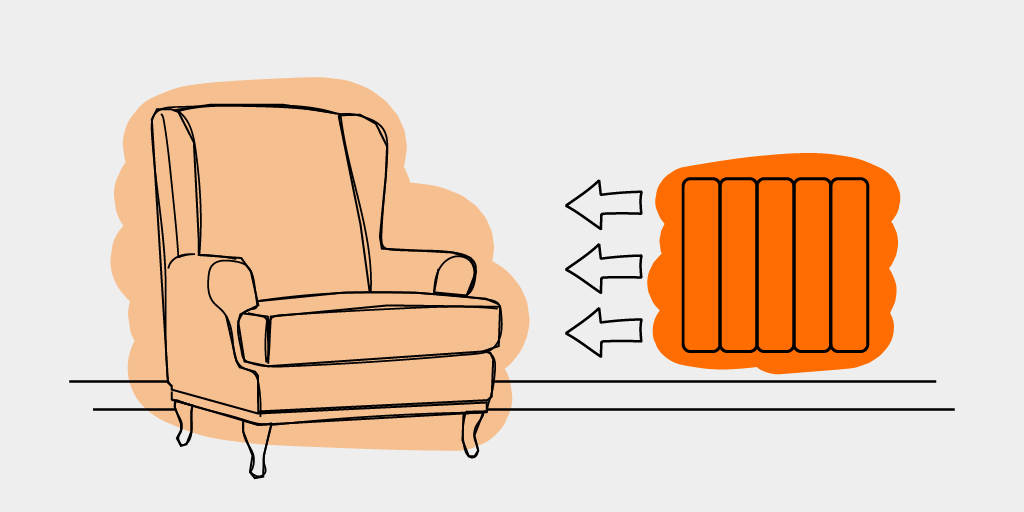

Radiation warms people and objects directly, moving from the heat source to the object in one simple energy transfer. Heating by radiation effectively cuts out the middle man in the heating process, allowing far less scope for energy loss.
Let’s take a deep dive into what makes electric radiators and panel heaters similar, different, and which one is perfect for your home if you’re weighing up your options.
Shop with confidence at Electric Radiators Direct
So there you have it. Hopefully now you’re more confident in differentiating between the two. Whether you’re interested in electric panel heaters, electric radiators, or electric conservatory heaters, be sure to check our store to find the best electric heater for your house today!
Key learnings
- Electric radiators and electric heaters look very similar and feature similar technologies, but there are key differences to consider.
- Electric heaters heat through convection and are designed for occasional heating. They're lightweight, portable and cheaper than electric radiators, but are inherently less efficient.
- Electric radiators heat through a combination of convection and radiation making them extremely efficient. They're ideal for use as a primary heat source.






